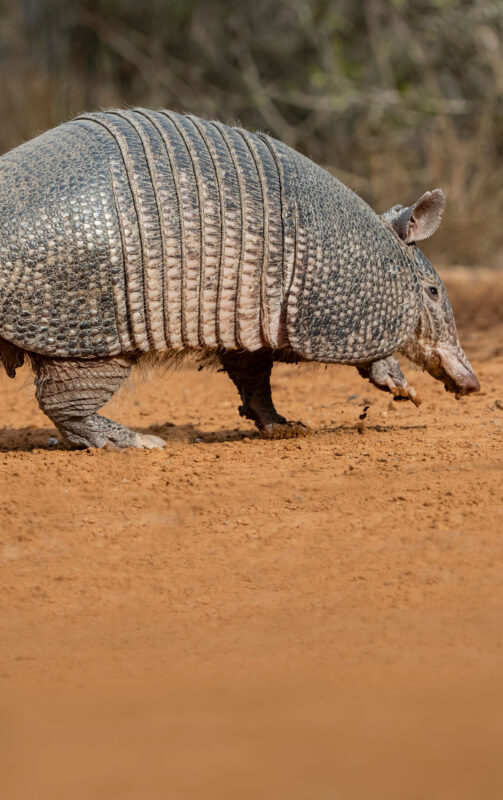
Armadillos
Disease
Armadillos can be infected by the bacterium Mycobacterium Leprae which is the causative agent of Leprosy. The role that armadillos have in human infections, however, has not been determined.
They may pose a potential risk for humans, particularly in the Gulf Coast region.
Armadillos
Management
Management
Armadillos have the ability to climb and burrow. Fencing or barriers may exclude armadillos under certain conditions. A fence with a portion buried can be effective. The cost of exclusion of a large area should be compared to the cost of trapping and the value of the resources being protected. Treating the damaged area with insecticides is seldom effective. Insecticides will eliminate the armadillo’s food source but they also eliminate the beneficial insects in the soil.
Armadillos will still create damage in search of food after a chemical treatment. Armadillo damage increases in managed areas in dry weather due to watering. One might say the smell of wet soil is the magnet for armadillos.
If you are currently experiencing armadillo damage give us a call for a free consultation.